Run a Free Internet Speed Test Here!
What is my internet speed, and How is it Measured?
Internet speed refers to the time it takes for data to transfer back and forth to your device from the web server through the router. Megabits per second (Mbps) is the standard measurement for network speeds. The number of Mbps measures the connection speed at which data is downloaded/uploaded from the internet to your devices.
What you pay for may be different from what you get. You should periodically check your current internet speeds to see what happens during slowdowns or loss of connectivity and regular usage. If you don’t see the speeds you’re paying for, it may be time to call your internet service provider.
How do I run my WiFi speed test online?
You can use our free internet Speed Test tool to test internet speed. First, run our internet speed test on a mobile or laptop connected to your WiFi network. Then connect a wired desktop or laptop computer to the Ethernet ports of your router. Then, run our online speed test with the new wired connection again, and compare the results to the initial WiFi speed test. It’s best to test your WiFi speed in different locations around your home or office. This will give you a clear picture of your WiFi speed and help you identify areas where your signal is weaker.
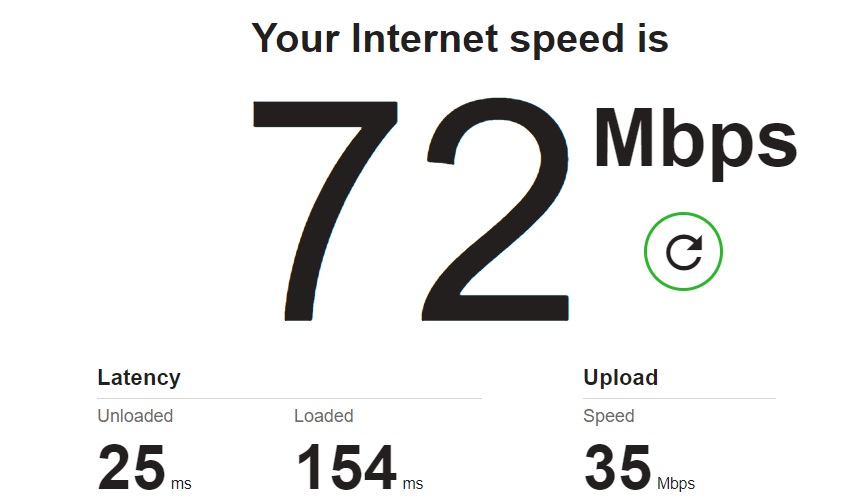
Result from an internet speed meter for PC.
Frequently Asked Questions in network speed test:
What’s the difference between download and upload speeds?
If you’re looking for Internet plans in your area, you’ll likely see two different speeds “download speed” and “upload speed.” Don’t be overwhelmed by the various numbers, but understand the difference. Here’s what you need to know:
Download speed:
Download speed is how fast your connection can get data from the internet (website, music, photos, etc.). For example, if you use your phone to watch a movie clip, it is the speed at which your computer loads the video.
Upload speed:
Upload speed is how fast your connection can send data from your computer/mobile to the internet. For example, upload speed would measure how long it would take you to post this adorable video of your baby on Facebook.
Key note:
Download speed is much more important to the average user as you only notice upload speed when trying to upload a large video. It’s fine if your check upload speed is about 10% of the download speed.
What is ping (latency)?
Ping, also called latency, is the time it takes for your network to transfer information from your computer to a remote server and vice versa. There will always be some latency in your network, but the lower this number, the better your performance. Online gamers should be particularly vigilant about ping, as high latency can cause a noticeable delay between their actions and the actions of other online players.
What is Jitter in an Internet connection?
Jitter is the deviation from the mean latency in an Internet connection. Jitter is important because it can affect the quality of voice and video transmissions. A high jitter means packets arrive late and out of order, which can cause choppy audio or video.
What is the difference between MB and Mbps?
Megabytes (MB) are a measure of binary data and are used to describe file size and digital storage capacity. A MB is larger than a kilobyte (KB) and smaller than a gigabyte (GB).
Megabits per second (Mbps) is a measure of how fast data is transferred, meaning it is used to describe internet bandwidth and speed. You will see this unit when you’re testing your network’s download and upload speeds.
How many devices should be connected to the network before an ISP speed test?
The number of devices connected to the network directly affects the speed test results. You should run the test with a single device and multiple devices to find the accurate result.
What is good internet speed?
There is no one answer to this question since everyone’s needs are different. However, a good general rule of thumb is that any internet connection that allows you to stream video and browse the web without too much lag is considered to be a good internet speed.
The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) has set the minimum standard for broadband internet as 25 Mbps for download and 3 Mbps for upload.
A good internet speed is about 100 Mbps download speed and 25 Mbps upload speed. It is enough for everyday activities such as watching movies, playing online games, and surfing websites. High-speed internet is about 200 Mbps+ download speed and 50 Mbps+ upload speed.
Why is my internet speed slower than expected?
There could be several reasons why your internet speed is slower than you expect. Your internet plan may need to be faster for your needs, your modem or router might need to be updated, your router may freeze, or too many people may be using your WiFi network simultaneously.
Try these methods to see if we can get a more accurate result:
- Restart your modem and router, and run the test again.
- Temporarily disable your firewall and run the test again.
- Disconnect your router from the modem, connect a desktop or laptop to the modem’s Ethernet port, and rerun our speed test.
- If you have a wireless gateway instead of a separate modem and router, connect a desktop or laptop to the Ethernet ports, and rerun the test.
You may have a bottleneck on your end if you see inconsistent results.
If you’ve tried all of these things and you’re still not getting the speeds you’re expecting, it’s possible that there’s an issue with your internet service provider. Contact them and let them know about the problem. They may be able to help you troubleshoot the issue or give you credit for the inconvenience.
Why do I get different results when I run the speed test multiple times?
Internet Speed Test is based on real-time network conditions that can change rapidly. As a result, tests performed within a few minutes of one another vary. Tests taken farther apart may differ even more due to network congestion and bandwidth availability. We recommend running the test a few times at different times of the day to get a better understanding of fluctuations that occur at specific times.
What Factors Affect Internet Speed?
There are many factors that can affect your internet speed. Your internet service provider (ISP) is one of the biggest factors, as they can throttle your speed or impose data caps. The type of internet connection you have can also affect your speed. For example, fiber optic internet is typically faster than cable or DSL.
In addition, your computer’s hardware can also affect your internet speed. If you have an old computer with a slow processor, you’re likely to experience more unhurried speeds than someone with a new computer. The same is true for your router – an old and outdated router can also slow down your speeds. Running multiple devices on the same network can impact overall Internet speeds.
Occasionally, the capabilities of a website or an Internet network can affect connection speed through bandwidth limitations. High-traffic websites can cause your Internet connection to run slower when you visit a specific domain.
Finally, the computer’s operation can affect your Internet access. The presence of a virus or a Trojan horse, a wrong firewall configuration, and the execution of specific procedures (update, saving, antivirus analysis, etc.) can slow down the network connection.
How can I improve my internet speed?
Restart your router or modem
Turn off your modem or wireless gateway, wait five minutes, and then turn it back on. If your wireless connection is still bad after rebooting your modem, try repeating the steps with your router. Finally, try turning off WiFi on all of your connected devices. Please wait a few minutes and then turn it back on. Wait for your current devices to connect and see if your internet speed improves.
Move your router to another location
Routers are affected by location. Consider placing your WiFi router close to your main TV viewing area for a better connection experience. Also, try to keep any walls between your router and your devices to a minimum. Certain appliances can hamper your router’s signal. Just place the router where a microwave won’t affect your WiFi.
Consider using a range extender
Depending on your home’s layout and your wireless router’s location, you may have trouble maintaining a strong internet signal. Range extenders is an inexpensive way to spread your wireless signal to cover the whole house. Expect to pay anywhere from $50 to $150 for a decent model. They allow you to place the unit closer to where you do most of your internet activity.
Outdated network hardware
Perhaps your modem or router are out of date? This sometimes affects your speed. Contact your internet service provider to make sure your network devices are up-to-date. In most cases, they will upgrade your setting for free. Your ISP maintains all 3rd-party equipment compatible with their internet service. Talk to them to find out which solution is best for you.
Looking for a new internet service provider
If you’re still unhappy with your internet speed, you can still change your ISP. ISPs typically offer several different types of technologies used for internet access. Some may be faster but cheaper than others.

